Quality control of cell lines
Quality control is important in the use of cell lines, for both reproducibility of results and safety concerns with biological products. All cell lines distributed from the JCRB Cell Bank have been confirmed as contaminant free and authenticated through the following quality control. The data obtained from the quality control testing is included in the information for each cell line on our website. Certificates of Analysis are issued for each cell line on request.
- Bacteria and fungi testing To assess contamination of bacteria and fungi in cell lines, cells are disseminated to three kinds of medium optimized for bacteria and fungi. Although the following culture conditions cover most bacteria and fungi, some microorganisms that require specific conditions cannot be detected in our tests. All cell lines for distribution have passed this test as being free of the contamination.
- Medium Blood ager with 5% rabbit blood
- Cultivation temperature: 35°C
- Cultivation period: 1 week – 2 months (depending on medium)
- Mycoplasma screening Mycoplasma contamination is a serious problem that can lead to erroneous data and cause unnecessary repetition of experiments. Our routine procedure to assess mycoplasma contamination consists of the following three methods.
- Mycoplasmal enzyme activity Measurement in culture supernatants is a rapid test to check for contamination.
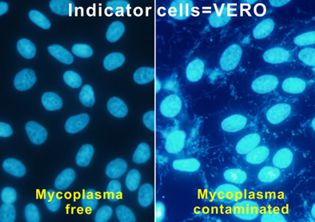
- Fluorescence staining using VERO cells Supernatant samples are inoculated onto VERO cell culture (JCRB0111). After the 5-day culture, the cells are stained with Hoechst 33258 which detects nuclei of VERO cells as well as mycoplasmal DNA. If positive for mycoplasma, additional fluorescence is observed around the nuclei, showing spider web-like structures. Contamination of bacteria and fungi can also be observed by this method.
- Nested-PCR Amplification of mycoplasmal DNA is performed using two sets of primers, which improves sensitivity and specificity.
- Cell line authentication Human cell lines are identified based on Short Tandem Repeat (STR) profiles by PCR.
- Viral examination Human cell lines are screened for 16 pathogenic viruses by targeting viral DNA and/or RNA fragments. This consists of 10 DNA and 6 RNA viruses.Virus positive results in this assay do not necessarily indicate virus-producing cells. Some cell lines registered before 2006 have not been examined and are in progress.
- DNA fragments Testing Method: Real-time TaqMan PCR assay (positive control:GAPDH)
- RNA fragments Testing Method:Real-time TaqMan RT-PCR assay (positive control:β-actin)
- Species identification Animal cell lines can be identified for their origin of species by isozyme analysis. This was done until 2012, but is not currently examined due to discontinuation of the reagent.
- Chromosome analysis The number of chromosomes is counted on Giemsa-stained metaphases, which reveals differences between cells in the heterogeneous population. Karyotyping is performed by G-banding, which identifies chromosome rearrangements characterizing each cell line. These data are limited to certain cell lines.
Nutrient broth with 2% yeast extract (NB medium)
Thioglycolate broth (TGC medium)
Reagent:MycoAlert™ Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Lonza, LT07-318) ☞
reference1☞
reference2☞
A list of cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines
Reagent:PowerPlex®16 System (Promega, DC6530) ☞
Extraction reagent:AllPrep DNA/RNA mini kit
Target viruses:CMV, EBV, HHV-6, HHV-7, BKV, JCV, ADV,
B19V (parvoB19), HBV, HTLV-1, HTLV-2, HIV-1,
HIV-2, HAV
Target viruses:HCV, HTLV-1, HIV-1, HTLV-2, HIV-2, HAV
Reference☞